Dopamine — Dopamine (Intropin®) has a variety of effects depending upon the dose range administered:
- At doses of 1 to 2 mcg/kg per minute, dopamine acts predominantly on dopamine-1 receptors in the renal, mesenteric, cerebral, and coronary beds, resulting in selective vasodilation. Some reports suggest that dopamine increases urine output by augmenting renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate, and natriuresis by inhibiting aldosterone and renal tubular sodium transport [18-20]. These effects may be blunted by haloperidol and other butyrophenones [20]. However, the clinical significance of these phenomena is unclear, and some patients may develop hypotension at these low doses [21]. (See “Renal actions of dopamine”).
- At 5 to 10 mcg/kg per minute, dopamine also stimulates beta-1 adrenergic receptors and increases cardiac output, predominantly by increasing stroke volume with variable effects on heart rate [22]. Doses between 2 and 5 mcg/kg per minute have variable effects on hemodynamics in individual patients: vasodilation is often balanced by increased stroke volume, producing little net effect upon systemic blood pressure. Some mild alpha adrenergic receptor activation increases SVR, and the sum of these effects is an increase in MAP.
- At doses >10 mcg/kg per minute, the predominant effect of dopamine is to stimulate alpha-adrenergic receptors and produce vasoconstriction with an increased SVR [22,23]. However, the overall alpha-adrenergic receptor effect of dopamine is weaker than that of norepinephrine, and the beta-1 adrenergic receptor stimulation of dopamine at doses >2 mcg/kg per minute can result in dose-limiting dysrhythmias.
In practical terms, the dose-dependent effects of dopamine mean that increasing the dose of the drug is akin to switching vasopressors. Conversely, simply increasing the dose of dopamine without being cognizant of the different receptor populations activated can cause untoward results.
The usual dose range for dopamine is 2 to 20 mcg/kg per minute, although doses as high as 130 mcg/kg per minute have been employed [24]. Dopamine is most often used in hypotension due to sepsis or cardiac failure, where it should be started at 2 mcg/kg per minute and then titrated to a desired physiologic effect rather than a predicted pharmacologic range. Such titration is necessary because weight-based administration of dopamine can achieve quite different serum drug concentrations in different individuals [25].
Dobutamine — Dobutamine (Dobutrex®) is not a vasopressor but rather is an inotrope that causes vasodilation. Dobutamine’s predominant beta-1 adrenergic receptor effect increases inotropy and chronotropy and reduces left ventricular filling pressure. In patients with heart failure this results in a reduction in cardiac sympathetic activity [26]. However, minimal alpha- and beta-2 adrenergic receptor effects result in overall vasodilation, complemented by reflex vasodilation to the increased CO. The net effect is increased CO, with decreased SVR with or without a small reduction in blood pressure.
Dobutamine is most frequently used in severe, medically refractory heart failure and cardiogenic shock and should not be routinely used in sepsis because of the risk of hypotension. Dobutamine does not selectively vasodilate the renal vascular bed, as does dopamine at low doses. (See “Inotropic agents in heart failure due to systolic dysfunction”).
Uptodate.com 참고.
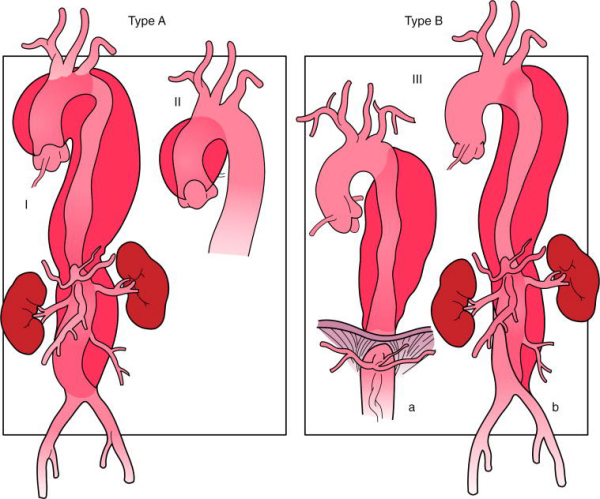

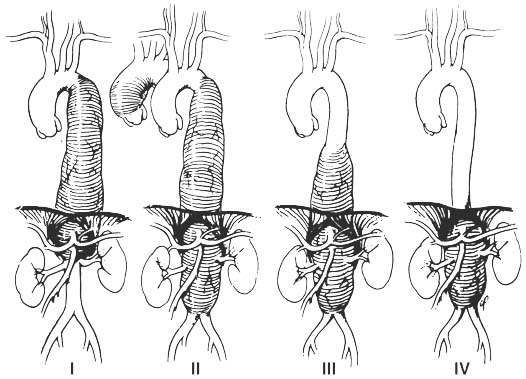
 Thoracoabdominal aorta aneurysm 을 분류하는 기준에 Crawford classification이 있다. 수술 후의 합병증으로 고생하시는 분들도 있지만 걸어서 퇴원하시는 분들도 있다. 중환자실에서 2~4일 정도 있다가 병동에서 1주일 정도면 퇴원을 하는 것을 보고 있으면 놀랍다는 생각밖에는 들지 않는다.
Thoracoabdominal aorta aneurysm 을 분류하는 기준에 Crawford classification이 있다. 수술 후의 합병증으로 고생하시는 분들도 있지만 걸어서 퇴원하시는 분들도 있다. 중환자실에서 2~4일 정도 있다가 병동에서 1주일 정도면 퇴원을 하는 것을 보고 있으면 놀랍다는 생각밖에는 들지 않는다.