- 병동 당직 상황에서 혈압을 낮추는 방법에 대해서는 지난 번에 찾아 보았다.
- 그보다는 드물지만 혈압을 올려야 하는 상황에 대하여 알아보고 싶었다.
- 페이스북을 통하여 외상 전문의에게 물어 봤더니 norepinephrine 이 기본이라고 한다.
- Uptodate 에 언급하는 사용 방법은 다음과 같다.
- 초기 용량
- 5 to 15 mcg/min (0.05 to 0.15 mcg/kg/min)
- Cardiogenic shock: 0.05 mcg/kg/min
- 유지 용량
- 2 to 80 mcg/min (0.025 to 1 mcg/kg/min)
- Cardiogenic shock: 0.05 to 0.4 mcg/kg/min
- 최대 용량
- 80 to 250 mcg/min (1 to 3.3 mcg/kg/min)
- 역할
- Initial vasopressor of choice in septic, cardiogenic, and hypovolemic shock.
- Wide range of doses utilized clinically.
- Must be diluted; eg, a usual concentration is 4 mg in 250 mL of D5W or NS (16 micrograms/mL).
- 초기 용량
Category: 03_Study
-
Norepinephrine
-
위암 고식적 요법 1차
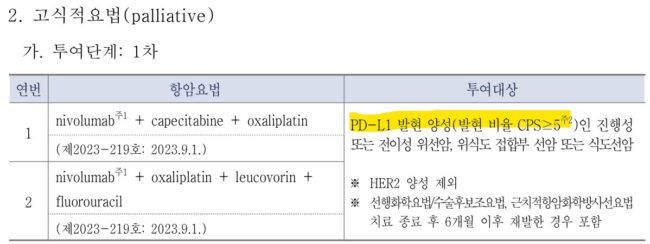
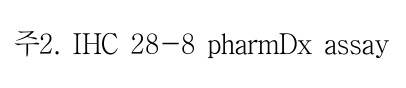
위암에서 옵디보(nivolumab)를 사용하기 위해서는 28-8 검사를 해야 한다.
-
Nitroglycerin
NTG를 너무 아껴 드시는 것 같은 분이 있었다. 그래서 도대체 언제쯤 먹어야 하는지 찾아봤다. 살짝 느껴도 먹어야 하는지도 궁금했다. 정답은 모르겠다. Mayo Clinic 웹사이트에서는 다음과 같이 표현했다.
NTG를 너무 아껴 먹을 필요는 없을 것 같다.

-
The Management of Elevated Blood Pressure in the Acute Care Setting: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
- 원인
- 만성 고혈압이 조절이 안되고 있음
- 코티졸이나 카테콜아민 증가
- 혈압을 올릴 수 있는 약물 사용
- NSAID, 스테로이드 등
- 집에서 먹던 약을 안 먹음
- 혈압 측정 오류
- 수면 부족
- 급성 스트레스
- 통증, 불안 등
- Volume overload 등 clinical condition
- 치료
- 표적 장기 손상이 있을 것으로 보이는 장기에 따라 다름
- Labetalol, nicardipine 등을 주로 사용할 수 있음
The Management of Elevated Blood Pressure in the Acute Care Setting: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association | HypertensionOver the past 3 decades, a substantial body of high-quality evidence has guided the
diagnosis and management of elevated blood pressure (BP) in the outpatient setting.
In contrast, there is a lack of comparable evidence for guiding the management of
elevated BP in the acute care setting, resulting in significant practice variation.
Throughout this scientific statement, we use the terms acute care and inpatient to
refer to care received in the emergency department and after admission to the hospital.
Elevated inpatient BP is common and can manifest either as asymptomatic or with signs
of new or worsening target-organ damage, a condition referred to as hypertensive emergency.
Hypertensive emergency involves acute target-organ damage and should be treated swiftly,
usually with intravenous antihypertensive medications, in a closely monitored setting.
However, the risk-benefit ratio of initiating or intensifying antihypertensive medications
for asymptomatic elevated inpatient BP is less clear. Despite this ambiguity, clinicians
prescribe oral or intravenous antihypertensive medications in approximately one-third
of cases of asymptomatic elevated inpatient BP. Recent observational studies have
suggested potential harms associated with treating asymptomatic elevated inpatient
BP, which brings current practice into question. Despite the ubiquity of elevated
inpatient BPs, few position papers, guidelines, or consensus statements have focused
on improving BP management in the acute care setting. Therefore, this scientific statement
aims to synthesize the available evidence, provide suggestions for best practice based
on the available evidence, identify evidence-based gaps in managing elevated inpatient
BP (asymptomatic and hypertensive emergency), and highlight areas requiring further
research. - 원인
